Farm or Ranch? It’s quite common to mix up these terms and use them interchangeably.
So, what really is the difference? If you’ve ever wondered, you’re not alone.
Let’s delve into this age-old conundrum, highlighting key differences and providing a fresh perspective.
Understanding the Basics
Farm…Ranch…terms that relate to the land, ostensibly used in the context of agriculture.
However, while they do share similarities, their differences lie in nuances.
1. Farms: A Broad Spectrum
A farm is a piece of land primarily used for growing crops, raising livestock, dairy production, poultry, or any other form of sustained agricultural activity with a clear focus on food production.
It is generally a self-sufficient entity, where everything produced often circles back into the farm’s operations or is sold for profit.
It means different things in different parts of the world but this basic rule applies universally.
2. Ranches: Specialization is Key
Ranches, on the other hand, are a type of farm that specializes in raising livestock like cattle, sheep, or horses, which are then sold as meat or products.
A ranch tends to involve a much larger tract of land compared to a typical farm because raising livestock necessitates more roaming and grazing space.
“Think of a farm like a buffet restaurant with a wide variety of food on offer, while a ranch is more of a specialized steakhouse.”
Key Features: Farms vs. Ranches
Let’s take a closer look at the operational aspects which are the key differentiators between farms and ranches.
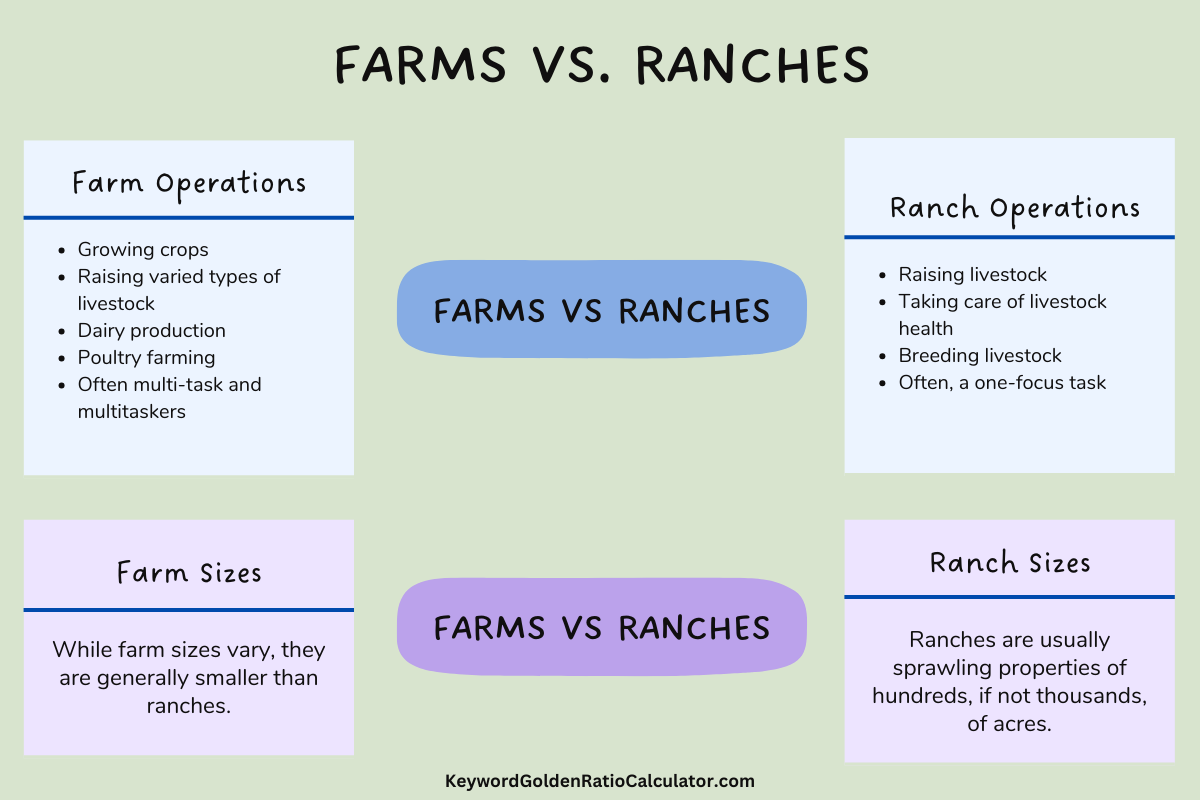
1. Farm Operations
Farm operations involve numerous activities such as:
- Growing crops
- Raising varied types of livestock
- Dairy production
- Poultry farming
- Often multi-task and multitaskers
Farmers are typically multitaskers, dealing with a broad range of activities and responsibilities daily, centering around multiple aspects of agriculture.
2. Ranch Operations
Ranch operations focus largely on:
- Raising livestock
- Taking care of livestock health
- Breeding livestock
- Often, a one-focus task
Ranchers’ tasks mainly revolve around managing livestock, ensuring their health, and preparing them for eventual sale.
Scopes and Sizes: How Big is Big Enough?
Another difference between a farm and a ranch lies in the land size and scope of operation.
1. Farm Sizes
While farm sizes vary, they are generally smaller than ranches.
In theory, a sizable backyard could qualify as a farm if it produces some form of agricultural product.
2. Ranch Sizes
Ranches are usually sprawling properties of hundreds, if not thousands, of acres.
The vast size of a ranch does not necessarily equate to higher productivity but provides the necessary space for livestock to graze freely.
Livelihood: The Money Talks
The difference between the farm and the ranch continues even in the avenues of income generation.
1. Farm Livelihood
Farms sell products generated from multiple sources such as crops, dairy, fruits, vegetables, and more.
Thus, their income streams are more diverse.
2. Ranch Livelihood
Ranches earn primarily from selling livestock as meat or products derived from them, which creates a more focused revenue stream.
In Conclusion: Celebrating Diversity in Agriculture
To sum up, both farms and ranches are essential elements of our agriculture system.
They might have similar essences, but each brings unique strengths to the table.
Therefore, while they might seem alike at first glance, the farm-ranch dichotomy is defined by functional, operational, and financial differences.
So next time you find yourself muddled between a farm and a ranch, remember this:
Farms offer a diverse array of agricultural activities, whereas ranches specialize in the business of raising livestock.
Now that you’ve unraveled the ranch and farm conundrum, why don’t you share this newfound knowledge with your friends or maybe start a conversation the next time you visit either a farm or a ranch?
Trust us, it’s an incredible conversation-starter!
FAQs – What is the Difference Between a Ranch and a Farm?
What is a farm?
A farm is a type of agricultural land where crops are grown or animals are raised. This can include a variety of types such as dairy farming, orchards, vineyards, or raising livestock like cattle or poultry.
What is a ranch?
A ranch is a subtype of farm that primarily specializes in large-scale livestock operations. Ranchers raise animals, such as cattle or sheep, usually for meat or wool production. They have vast open lands for grazing.
Is a ranch always bigger than a farm?
Not necessarily. The size difference between a ranch and a farm can vary greatly. While ranches often tend to cover vast areas of land for animal grazing, farms can range from small plots to very large properties, too. The primary difference is what they’re used for rather than their size.
Can crops be grown on a ranch?
Yes, crops can be grown on a ranch, but it’s usually done to support the livestock, not for selling the crops commercially. Ranches focus on raising livestock, and any cropland typically serves to supplement the animals’ diet.
Can animals be raised on a farm?
Yes, animals can be raised on a farm. Many farms raise animals, but they also typically grow crops. Farms tend to have greater diversity with both animals and crops, unlike ranches, which focus mostly on livestock.
Is the difference between a farm and a ranch based on geographical location?
No, the difference is not based on the geographic location, but rather on their primary function. You can find both farms and ranches in many parts of the world. However, the term “ranch” is more commonly used in Western US and Canada.
What does cattle ranching involve?
Cattle ranching involves raising, grazing, and sometimes breeding cattle. The cattle are primarily raised for meat and dairy products. Ranchers are primarily responsible for animal health, overseeing grazing, and maintaining the land.
What types of farms are there?
There are many types of farms depending on what they produce. Some farms focus on growing fruits or vegetables, known as orchards or market gardens. Others, like dairy farms, raise animals for milk production. Some farms may even focus on beekeeping for honey production, known as apiaries.
Are there regulatory differences between farms and ranches?
Yes, there can be. The rules and regulations for farming and ranching can differ based on factors such as the types of animals raised, the crops grown, environmental practices, and more. It’s crucial for both farmers and ranchers to understand and comply with these regulations.
How can one transition from farming to ranching or vice versa?
The transition from farming to ranching or vice versa would require changes in land use, equipment, knowledge, and possibly regulatory compliance. It could involve a significant investment of time and resources. Therefore, one must carefully consider the implications and requirements before making such a transition.